08/01/2021 posted
Spurious
Spurious may refer to the entire part other than the intentional output signal, but generally refers to the unnecessary signal that are not random noise, such as identifiable crosstalk and power coupling.
There are two types of spurious in a function generator: harmonic spurious and non-harmonic
spurious. The harmonic spurious is an integral multiple of the fundamental wave and is directly
related to the total harmonic distortion.
The non-harmonic spurious refers to the part that are not in an integer ration with the
fundamental wave, such as the CPU clock inside the signal generator and the power supply
switching pulse.
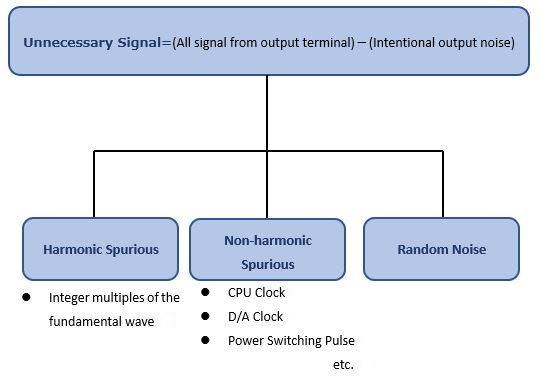
Fig1. Unnecessary Signal
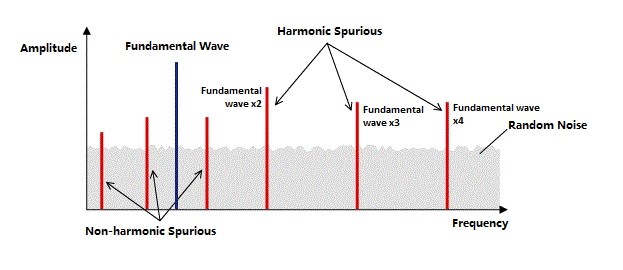
Fig2. Spectrum Diagram at sine wave output
The spurious performance of a signal generator is generally expressed in decibels, which is the
ratio of the carrier wave (the intentional output signal) to the spurious component. The unit is
[dBc]. In the specifications, the output frequency band is divided into several and each
defined.
For instance, it is expressed as -60 dBc or less at 1 MHz or less, and -50 dBc or less at 1 MHz
to 10 MHz.