08/01/2021 posted
Capacitive Coupling
There is always a capacitance between two unshielded conductors.
When the noise voltage en of frequency fn is coupled to the circuit with impedance Z through a
very small amount of capacitance Cs, the mixed noise voltage becomes the value below:
(Cs is proportional to area and inversely proportional to distance)
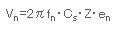
When the capacitive coupling cannot be ignored, the signal source, connecting cable and noise
source shall be electrostatically shielded. That is, it is covered with a conductor and
connected to the reference potential.
Furthermore, it is also ideal to connect the surrounding conductors (metals) such as racks and
tables, to the reference potential. And electric charges are generated when the distance of the
part with potential difference fluctuates, so the part with high impedance or high voltage is
mechanically and firmly fixed.
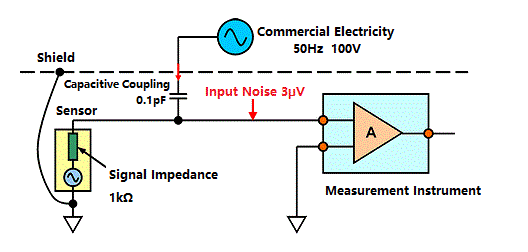
Even if the 100 V commercial electricity leaks into the signal impedance of 1 kΩ under the shielded measurement system, (with only a capacitive coupling of 0.1 pF) a noise of 3 µV will be mixed into the input of the measurement instrument.